Understanding Thumb Arthritis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
An Overview
Do you experience pain, swelling, or weakness at the base of your thumb, especially when gripping or pinching? You might have thumb arthritis, a common condition affecting the joint where your thumb meets your wrist.
What is Thumb Arthritis?
Thumb arthritis, also known as carpometacarpal (CMC) joint arthritis, is a type of arthritis that affects the cartilage in the joint at the base of your thumb. Cartilage is a smooth, rubbery tissue that cushions the bones in your joints and allows them to move smoothly. When this cartilage wears away due to age, overuse, or injury, the bones rub together, causing pain, swelling, and stiffness.
Causes
- Aging: This is the most common cause of thumb arthritis. As you age, the cartilage in your joints naturally breaks down.
- Previous injury: Fractures, sprains, or other injuries to the thumb joint can increase your risk of developing arthritis later in life.
- Repetitive stress: Activities that put repetitive stress on the thumb joint, such as gripping or pinching for long periods, can contribute to arthritis.
- Certain medical conditions: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis can also affect the CMC joint.
Symptoms
- Pain: This is the most common symptom and often worsens with activity, particularly gripping or pinching.
- Swelling: You might notice swelling at the base of your thumb, making it appear larger.
- Tenderness: The area around the joint might be tender to the touch.
- Stiffness: You might experience stiffness in your thumb, making it difficult to bend or move freely.
- Weakness: You might lose strength in your thumb, making it harder to grip objects.
- Grinding sensation: In some cases, you might feel a grinding sensation when you move your thumb.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will likely:
- Discuss your symptoms and medical history.
- Perform a physical examination to assess your thumb joint for tenderness, swelling, and motion.
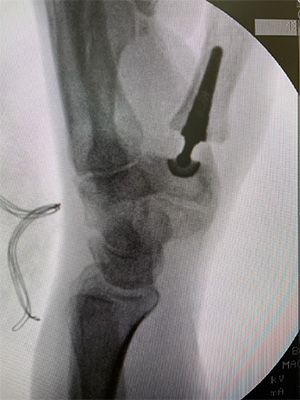
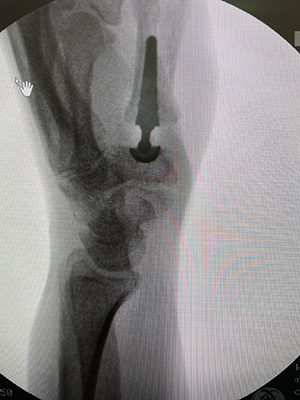
- Order X-rays to visualize the bones and check for any damage or bone spurs.
Treatment
There’s no cure for thumb arthritis, but various treatments can help manage the symptoms and improve your daily life. These include:
- Rest: Avoiding activities that aggravate the pain.
- Splinting: Wearing a splint to immobilize the joint and reduce inflammation.
- Ice therapy: Applying ice packs to the affected area to reduce pain and swelling.
- Pain medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers can help manage pain and inflammation.
- Physical therapy: Exercises to strengthen the muscles around the thumb and improve flexibility.
- Cortisone injection: Injections of a powerful anti-inflammatory medication to reduce pain and inflammation in the joint.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery might be considered to repair or replace the damaged joint.
Remember
Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent the condition from worsening. If you experience persistent thumb pain, consult your doctor to discuss the best course of action for you.