Understanding Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
An Overview
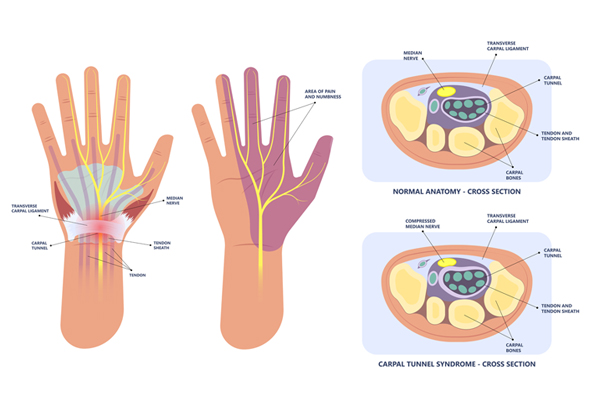
Do you experience tingling, numbness, or pain in your thumb, index, and middle fingers, especially at night? You might have carpal tunnel syndrome, a condition affecting the median nerve in your wrist.
What is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
The carpal tunnel is a narrow passage in your wrist where the median nerve and tendons share space. When the tissues around the median nerve swell, they can squeeze the nerve, causing pain, numbness, and weakness in your hand. While the exact cause is often unclear, various factors can contribute:
- Increased pressure: Pregnancy, obesity, certain medical conditions (arthritis, diabetes) can cause swelling in the wrist.
- Repetitive hand movements: Jobs or activities involving prolonged grasping or wrist bending can irritate the nerve.
- Wrist injuries: Fractures or dislocations can damage the carpal tunnel.
Symptoms
- Numbness, tingling, or burning sensation: This typically affects the thumb, index, and middle fingers, often worse at night.
- Weakness and clumsiness: Difficulty gripping objects due to weakened hand muscles.
- Pain: May radiate from the wrist up the forearm.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will likely:
- Discuss your symptoms and medical history.
- Perform a physical examination to assess your hand and wrist function.
- Order tests like:
- X-rays: To rule out other conditions like bone fractures or arthritis.
- Ultrasound: To visualize the median nerve and surrounding structures.
- Electromyography (EMG) and Nerve Conduction Study (NCS): To measure the electrical activity of the muscles and nerves, helping confirm nerve compression.
Treatment
Treatment focuses on relieving pressure on the median nerve and preventing further damage. Non-surgical options include:
- Wrist splinting: Wearing a splint at night to keep your wrist in a neutral position.
- Activity modification: Avoiding repetitive hand movements or using ergonomic tools.
- Anti-inflammatory medication: To reduce swelling and pain.
- Physical therapy: Exercises to improve flexibility and strength.
- Steroid injections: Injections to reduce inflammation around the nerve.
If these methods don’t offer sufficient relief, surgery might be considered. This typically involves creating more space in the carpal tunnel to alleviate pressure on the median nerve.
Remember
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for preventing permanent nerve damage and regaining full hand function. If you experience persistent hand or wrist pain, consult your doctor to discuss the best course of action for you.