Elbow Fractures – What to Expect and How to Heal Efficiently
An elbow fracture can significantly disrupt your daily activities, from getting dressed and typing to lifting basic household items. Understanding the recovery time for a fractured elbow, along with the factors that influence healing, can help patients set realistic expectations, plan effectively, and actively participate in their rehabilitation journey. This article explores typical healing timelines, contributing factors, and strategies to support a safe and successful recovery.
(Radiograph showing a complex Elbow fracture fixed with a plate)
Understanding Elbow Fractures
The elbow joint is formed by the articulation of three bones: the humerus (upper arm bone), the radius, and the ulna (forearm bones). Fractures can involve one or more of these bones and vary in severity.
Common types of elbow fractures include:- ( https://shoulderelbow.co.uk/conditions/shoulder-and-elbow/shoulder-and-elbow-fractures/)
- Olecranon fracture – affects the bony tip of the elbow (part of the ulna)
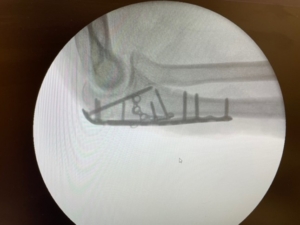
- Radial head fracture – involves the top of the radius bone near the elbow Radiograph showing Radial Head fracture fixed with a screw
(Radiograph showing Radial Head fracture fixed with a screw)
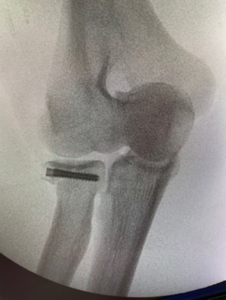
- Distal humerus fracture – occurs in the lower end of the upper arm bone Radiographs show Distal Humerus fracture treated with Plating
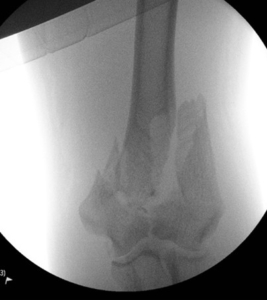
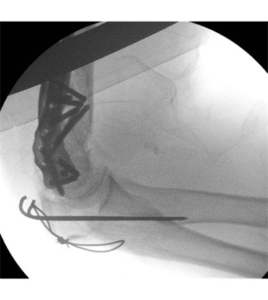
(Radiographs show Distal Humerus fracture treated with Plating)
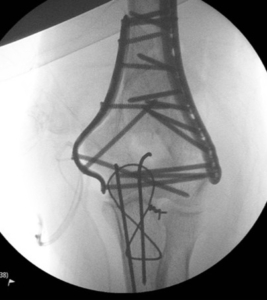
- Complex fractures – involve multiple bones or joint surfaces and may include dislocations or soft tissue injuries
Radiograph showing complex fracture dislocation of Elbow
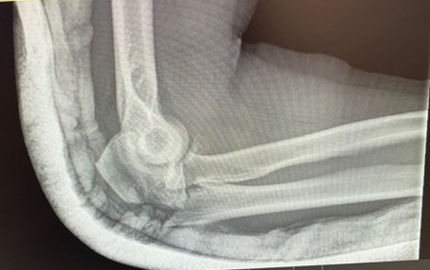
Picture6
Typical Recovery Time for a Fractured Elbow
Although each patient and injury is unique, the following general timelines offer a useful framework for recovery:
(Non-Displaced) Fractures
- Healing Time: 4to 6 weeks
- Treatment: Immobilisation with a sling or cast for few weeks; followed by guided physiotherapy
- Return to Normal Activity: Typically, 6 to 8 weeks
These fractures often heal without surgical intervention, especially with appropriate rest and rehabilitation.
Displaced Fractures
- Healing Time: 8 to 12+ weeks
- Treatment: May require surgical fixation using plates, screws, or pins
- Return to Normal Activity: Around 3 to 6 months
More severe injuries can involve damage to surrounding soft tissues. Surgical repair helps restore joint alignment and function but usually requires a longer recovery period
Factors That Influence Recovery Time
Several variables can affect how quickly an individual recovers from an elbow fracture:
- Type of Fracture
Displaced, compound, or comminuted fractures tend to have longer recovery times compared to simple or hairline fractures. - Patient Age and Overall, Health
Younger, healthier individuals often heal faster. Recovery may be delayed in older adults or those with underlying conditions such as diabetes, osteoporosis, or poor circulation. - Treatment Approach
Surgically treated fractures may initially require more recovery time but can lead to better long-term joint function when bones are properly realigned. - Adherence to Rehabilitation
Consistent participation in physical therapy is crucial. Lack of exercise or improper rehabilitation can lead to joint stiffness, reduced mobility, or incomplete recovery. - Lifestyle Factors
Smoking, poor nutrition, and non-compliance with post-operative or post-injury care can significantly delay the healing process.
Phases of Elbow Fracture Recovery
Weeks 1–3: Immobilisation and Pain Management
- Use of a splint, sling, or cast
- Common symptoms: swelling, bruising, and pain
- Pain relief through prescribed medications and cold therapy
- Minimal movement to protect healing bones
Weeks 4–6: Early Mobilisation
- Regular follow-up and imaging to assess healing progress
- Initiation of gentle range-of-motion exercises under professional guidance
- Progressive reduction in immobilisation
Weeks 7–12: Functional Rehabilitation
- Structured physiotherapy focusing on regaining strength and flexibility
- Gradual return to light activities, such as desk work
- Lifting, pushing, or sports activities are generally still restricted
3 Months and Beyond
- Most patients regain the ability to perform daily tasks
- Ongoing strength training and stretching may be required
- Full recovery, particularly after severe injuries or surgery, may take up to 6 months or longer
Tips to Enhance Recovery Time for a Fractured Elbow
To support optimal healing:
- Follow your orthopaedic surgeon’s guidance precisely
- Maintain a well-balanced diet rich in calcium, vitamin D, and protein
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Stay active within recommended limits to prevent stiffness
- Commit to your physiotherapy schedule and perform exercises as prescribed
- Allow your body time to heal without rushing the process
When to Seek Medical Attention?
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience:
- Persistent or worsening swelling, redness, or warmth around the elbow (signs of infection)
- Severe, unrelieved pain
- Numbness, tingling, or weakness in the fingers or hand
- Ongoing difficulty moving the elbow weeks into rehabilitation
Surgical treatment from Mr Singh
Whether you are having an injury or any chronic conditions, Mr Jagwant Singh can assist in fixing it all. He is a highly respected shoulder and elbow surgeon in London, known for his expertise in treating complex elbow injuries and disorders. With years of surgical experience and a commitment to patient-centred care, he has helped countless individuals regain mobility and improve their quality of life.
Conclusion
The recovery time for a fractured elbow can range from several weeks to several months, depending on the severity of the injury and the treatment method used. With expert medical care, a structured rehabilitation plan, and commitment to physiotherapy, most individuals can expect a full return to function and mobility.

Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!