Arthroscopy of the elbow: A Joint Problem Solution with Little Invasion
When your elbow hurts or is stiff, it can be hard to do easy things like turn the doorknob or do sports moves like throwing a ball. Elbow arthroscopy may be suggested if non-surgical methods like physical therapy, medicine, or shots don’t help reduce the pain. This minimally invasive surgery method is a precise and effective way to find and treat several elbow joint problems, with faster recovery times.
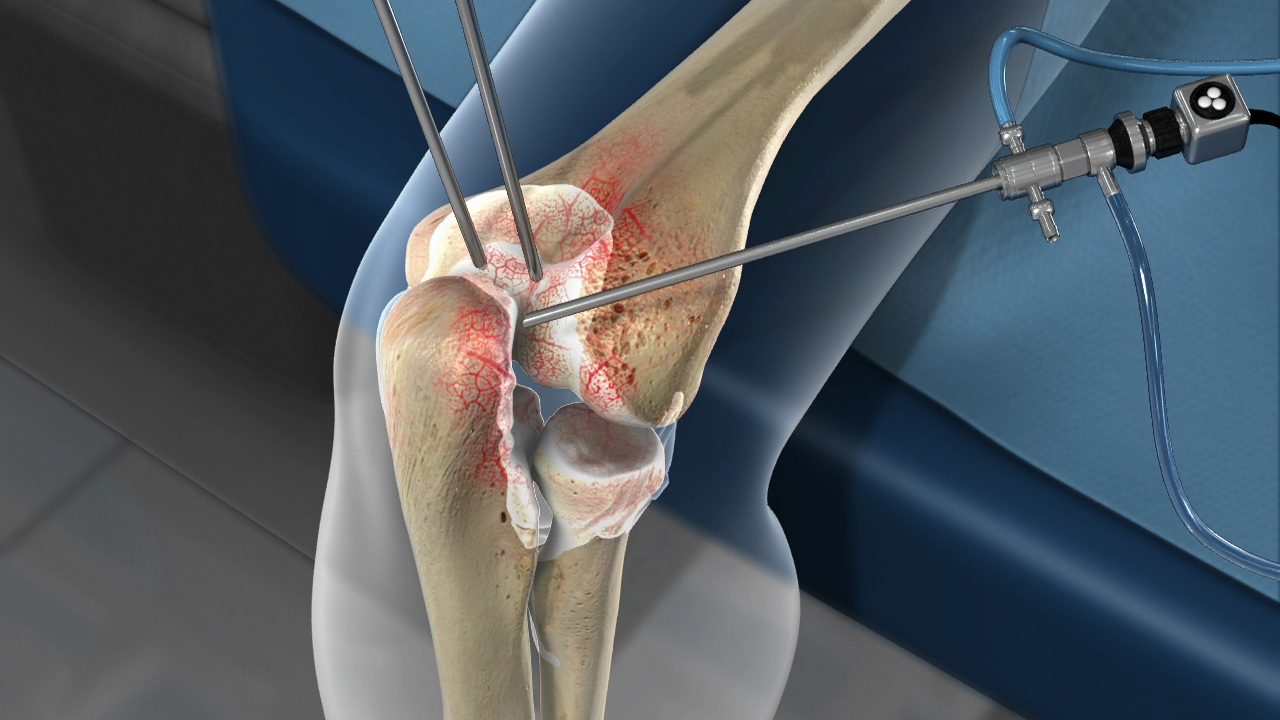
Understanding Elbow Arthroscopy!
In arthroscopy, a small camera called an arthroscope is used to look inside the joint. Unlike traditional open surgery, arthroscopy has fewer cuts, hurts tissues less, and most people heal faster and feel less pain after surgery.
When is it recommended?
Patients usually think about elbow arthroscopy when non-invasive treatments stop working or when an exact diagnosis is needed. Numerous health problems can be cured with it, such as:-
- Loose bodies (small fragments of bone or cartilage that float within the joint)
- Elbow arthritis (both rheumatoid and osteoarthritis)
- Tendon and ligament injuries
- Synovitis (inflammation of the joint lining)
- Stiff or locked elbow
- Bone spurs
- Osteochondritis dissecans
What to Expect from the Process?
Arthroscopy of the elbow is usually performed under general anaesthesia or regional nerve blocks. The patient’s arm is positioned to allow optimal access to the elbow joint. A tourniquet is often used to reduce bleeding and improve visibility inside the joint.
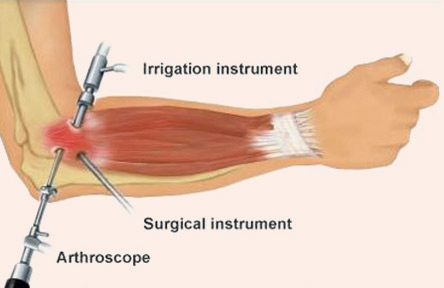
The surgeon makes small incisions (portals) around the elbow to insert the arthroscope and surgical instruments. Saline fluid is pumped into the joint to expand it and improve visualisation. Depending on the condition, the surgeon can remove loose bodies, shave bone spurs, smooth damaged cartilage, or repair ligaments and tendons.
The entire procedure typically takes 60 to 90 minutes, depending on the condition being treated. Most patients can return home the same day.
Recovery After Elbow Arthroscopy
Recovery varies depending on the condition being treated and the extent of the surgery. After the procedure:-
- The elbow is usually placed in a soft dressing or sling for support.
- Physical therapy may begin within a few days to restore range of motion and strength.
Most people can resume light activities within 1–2 weeks, while full recovery and return to sports or heavy labour may take 6–12 weeks.
Your surgeon will provide a customised rehabilitation plan based on the procedure performed and your personal goals.
Benefits of Arthroscopy
- Minimally invasive: Small incisions mean less pain, less risk of infection, and quicker recovery.
- Precise diagnosis and treatment: Surgeons can visualise and treat joint issues in real-time.
- Outpatient procedure: Most cases do not require overnight hospitalisation.
- Faster return to regular activity compared to open surgery.
Risks and Considerations
As with any surgical procedure, elbow arthroscopy carries some risks, including:-
- Infection
- Nerve or blood vessel injury
- Stiffness or limited motion post-surgery
- Temporary swelling or bruising
However, complications are rare, and the procedure’s benefits generally outweigh the risks when performed by an experienced orthopaedic surgeon.
Conclusion
Arthroscopy can help restore function, ease pain, and improve your quality of life, whether you’re an athlete with a repetitive stress injury or someone with arthritis.
If you’re experiencing ongoing elbow pain or stiffness, consult an orthopaedic specialist to determine whether elbow arthroscopy is the right solution for your problems.

Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!